Traditional network security models are no longer sufficient to protect against advanced cyber threats that frequently target large organizations. These threats often come from both external and internal sources, making it difficult to rely on perimeter defenses alone. In addition, the increasing use of cloud services and mobile devices has made it challenging to control access to sensitive data and applications.
To address these challenges, Zero Trust is the next evolution/addition in protecting networks and systems from insider threats and our adversaries. With zero-trust security, every user and device must be verified and authorized before being granted access to any network resource, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter. This approach requires strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and multifactor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information and systems.
Implementing a zero-trust security model introduces a new component that provides additional protection against cyber threats and increases the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical assets. By assuming that every user and device is a potential threat and requires continuous authentication and authorization, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes that no user, device, or network should be trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside an organization’s perimeter.
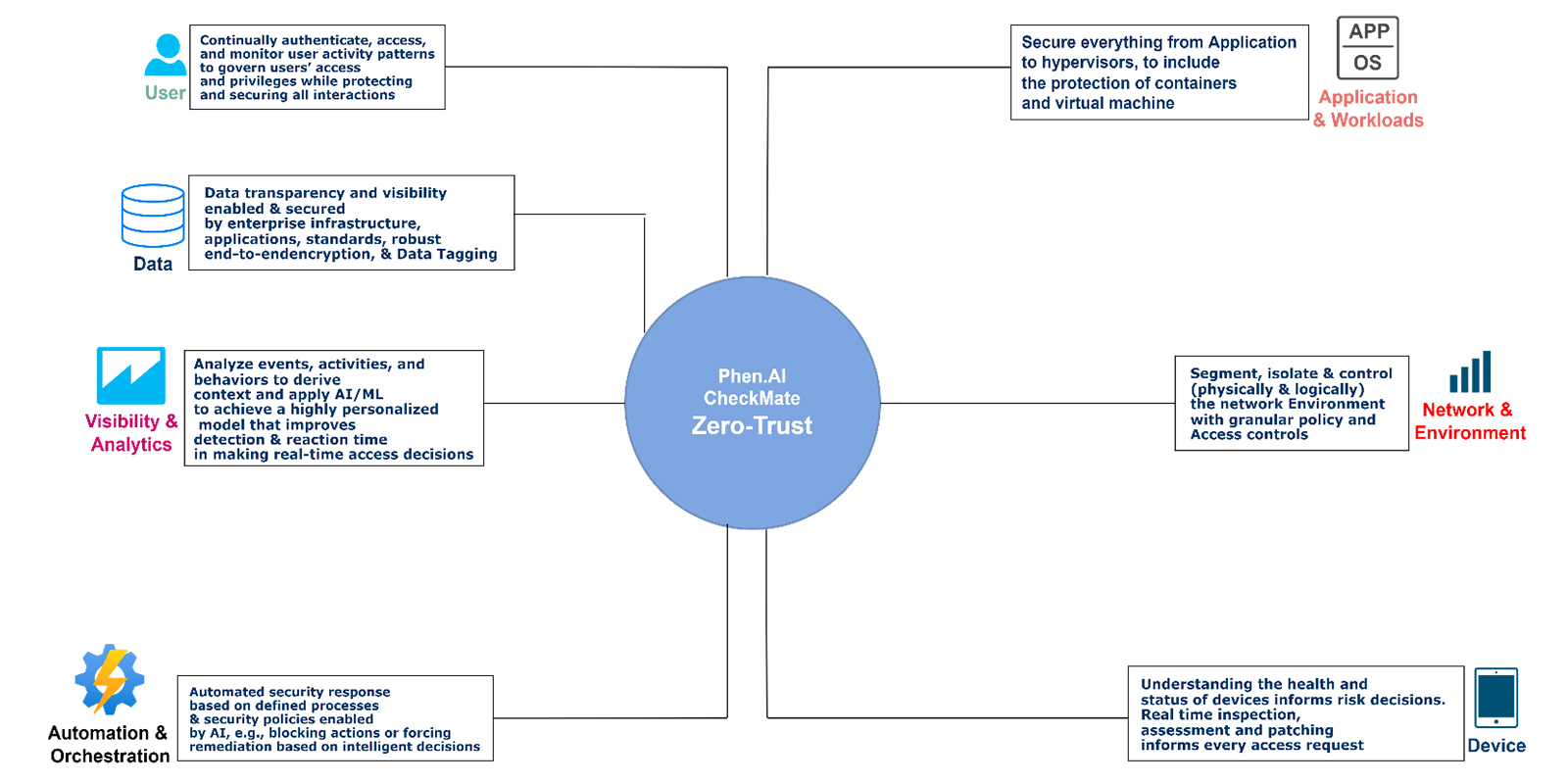
There are seven pillars of Zero Trust that organizations must consider when implementing this security model. These pillars include identity and access management (IAM), network segmentation, least privilege, data security, visibility and analytics, automation, and governance. Each pillar represents a different aspect of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) and is critical to the overall effectiveness of the security model.
In addition to these seven pillars, Zero Trust also includes several key capabilities that are necessary for effective implementation. These capabilities include multi-factor authentication (MFA), conditional access, micro-segmentation, and real-time monitoring. These capabilities help organizations protect against cyber threats by providing additional layers of security and increasing the organization’s ability to detect and respond to potential threats.
The maturity of Zero Trust can be measured in several ways. This includes the level of implementation of each of the seven pillars, the extent to which the organization has implemented the key capabilities of Zero Trust, the level of automation in the organization’s security processes, and the effectiveness of the organization’s security monitoring and response capabilities.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to enhance the effectiveness of Zero Trust by providing advanced threat detection and response capabilities. AI can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to identify potential threats and can also automate certain security processes to reduce the likelihood of human error. AI can be integrated with Zero Trust in several ways, including providing real-time threat detection and response capabilities, automating certain security processes, and enhancing the effectiveness of security monitoring and analysis tools.
In summary, Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no user, device, or network should be trusted by default, and it can help organizations protect against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. The maturity of Zero Trust can be measured in several ways, and AI can be used to enhance the effectiveness of Zero Trust by providing advanced threat detection and response capabilities.